
What are teeth and why do we need them?
Teeth play a big role in digestion. They cut and crush foods, making them easier to swallow.
While they look more like bones (but can’t repair like them), teeth are actually ectodermal organs (our others include our hair, skin and sweat glands).
Most adults have 32 permanent teeth (some are born with more or less).=
Four types of teeth
There are four types of teeth, and each does a different job, Incisors, Canines, Premolars and Molars
Incisors – front and centre
Our incisors are the most visible teeth in front of your mouth. Most people have four incisors on the upper jaw and four on the lower. These include your front two teeth and the teeth on either side of them.
Each incisor has a single narrow edge, which helps cut into food when you bite.
Canines – look like dog fangs
Canine teeth are pointier than other types of teeth. Most people have four canine teeth — one in each quadrant (upper right, upper left, lower right, lower left). Sometimes referred to as ‘eye teeth’ because of their position under your eyes
Canine teeth help you tear into foods like meat and crunchy vegetables.
Premolars – working both sides
Premolars (also called bicuspids) sit between your canines and your molars (the teeth in the back) and have features of both .
Premolars help you tear, crush and grind food into smaller pieces.
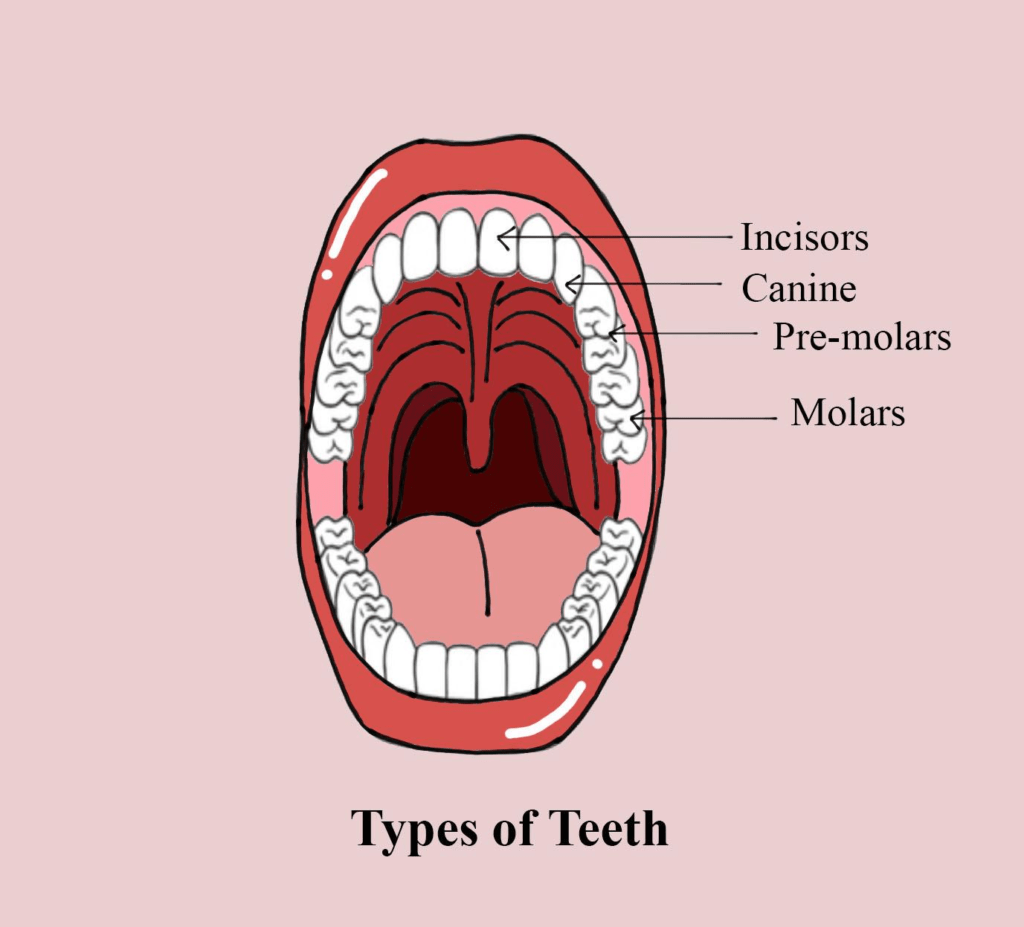
Molars – engine room
Molar teeth are in the very back of your mouth and most chewing happens there. Most adults have 12 molar teeth — three in each quadrant. Molar teeth include wisdom teeth (third molars). Molars are good for crushing and grinding up over 90% of your food.
Tooth structure
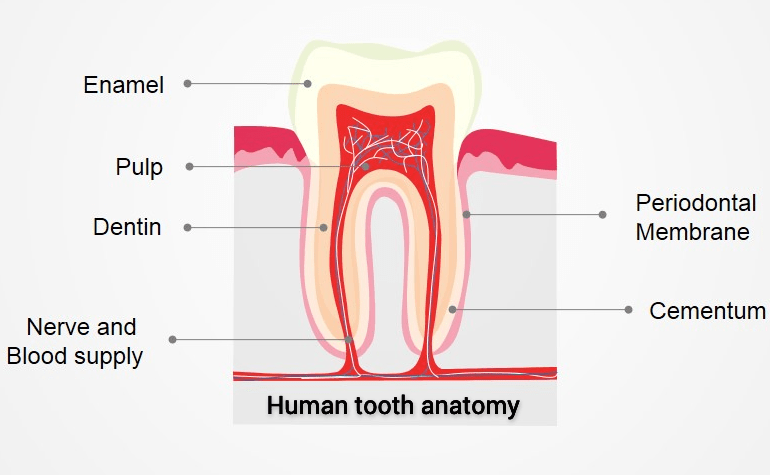
A tooth is divided into the crown, which is the part above the gum line, and the root, which is the part below the gum line.
The crown is covered with white enamel, which protects the tooth. Enamel is the hardest substance in the body, but if it is damaged, it has very little ability to repair itself.
Under the enamel is dentin, which is similar to bone but is harder. Dentin surrounds the central (pulp) chamber, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. Dentin is sensitive to touch and to temperature changes.
The blood vessels and nerves enter the pulp chamber through the root canals, which are also surrounded by dentin. In the root, dentin is covered by cementum, a thin bonelike substance.
Cementum is surrounded by a membrane (periodontal ligament) that cushions the tooth and attaches the cementum layer, and thereby the whole tooth, firmly to the jaw bone.
Most common dental problems
Dental problems usually fall into one of two categories—tooth decay and gum disease.
Cavities (Tooth Decay)
Cavities are caused by a breakdown of the tooth enamel by acids produced by bacteria located in plaque that collects on teeth.
Eating and drinking foods high in carbohydrates (sugar and starches) cause this bacteria to produce the acids that can cause the outer coating of the tooth (enamel) to break down (demineralize).
Untreated tooth decay can lead to abscess (a severe infection) under the gums which can potentially spread to other parts of the body.
Cavities are largely preventable, but remain one of the most common chronic diseases through our lifetimes.
Gum (Periodontal) Disease
Gum disease is mainly the result of infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth. Gingivitis is a milder form of gum disease that only affects the gums.
A US study showed about 4 in 10 adults aged 30 years or older had gum (periodontal) diseases in the five year period 2009–2014, and US dental health care is rated better than ours.
If not treated, the bone that supports the teeth can be lost, and the gums can become infected, teeth lose their bone support, become loose and may need to be removed.
Bruxism (teeth grinding).
Clenching and grinding your teeth can erode the enamel and make your teeth more susceptible to damage.
Teeth grinding is fairly common among users of Methamphetamine and MDMA. Science indicates this may be caused by an excess of serotonin in the nerve synapses which may lead to an inhibitory effect on the release of dopamine, which plays a major role in movement control.
Teeth grinding is linked strongly to stress, and taking steps to reduce this can reduce symptoms in many cases.
Teeth sensitivity.
Most of the time, teeth sensitive to heat and cold have worn enamel or exposed roots.
Trauma to your mouth.
Vehicular accidents, sports-related injuries and other traumas can lead to chipped, cracked or knocked-out teeth. Get them sorted. ACC can help in many cases.
Tooth discoloration.
It’s normal for some foods and drinks — such as tea, coffee or berries — to stain your teeth over time. You can also develop tooth discoloration from taking certain medications.
Whitening teeth has become very common both in dental practices and at home. Some of these products are better (or worse) than others and caution should be applied when being offered a new miracle whitening product.
Impacted teeth.
Sometimes teeth don’t erupt properly and they get stuck in your gums or jaw bone. The most common example is wisdom teeth impaction, though it can happen to any tooth.
Orthodontic misalignment.
Crooked, gapped, crowded or rotated teeth are all examples of orthodontic misalignment. These conditions can have a negative impact on your oral health and chewing function, as well as having a major impact on your smile and social confidence.
Abscessed tooth.
Sometimes bacteria invade the pulp — the innermost layer of your tooth. When this happens, you could develop a painful abscess (pocket of pus). This requires dental help and should not be left to get better. It won’t.


